Deploying an AI ChatBot in Azure Red Hat OpenShift fully integrated with Azure OpenAI
How can we integrate the power of Azure OpenAI and Azure Red Hat OpenShift in an easy and scalable way? How can we deploy a ChatBot in ARO using Azure OpenAI as a backend for our integrations? How can we leverage ARO as a Turnkey Application Platform to deploy and scale our ChatBot?
1. Overview
In this blog post, the primary focus is on creating a sophisticated ChatBot application with seamless integration into Azure OpenAI. The goal is to develop, build, and deploy a ChatBot that serves as a user-friendly FrontEnd, powered by Gradio, a Python library known for simplifying the creation and sharing of applications.
A crucial component enhancing this ChatBot’s capabilities is LangChain, a versatile framework tailored for building applications driven by language models. LangChain empowers applications to establish contextual awareness by connecting language models to various sources of context, such as prompt instructions, few-shot examples, and relevant content. This contextual understanding ensures the ChatBot’s responses are grounded effectively, enhancing user interaction.
The unique aspect of this ChatBot lies in its backend, where a robust GPT Model is deployed on Azure OpenAI. This integration ensures a smooth user experience, leveraging the capabilities of OpenAI’s cutting-edge technology within Azure’s reliable environment.
This integration highlights the power of Azure Red Hat OpenShift, which serves as the platform for deploying this ChatBot application. By harnessing the potential of Large Language Models like GPT, this blog demonstrates the innovative possibilities that arise when advanced AI technology meets the secure infrastructure provided by Azure OpenAI and Azure Red Hat OpenShift.
Throughout the blog, readers will find detailed steps on how to create and deploy such an application, making it a comprehensive guide for developers and enthusiasts eager to explore the synergy between Azure OpenAI and Azure Red Hat OpenShift.
The blog aims to inspire and empower readers to harness the full potential of AI-driven applications while ensuring a seamless integration process, from development to deployment, in the Azure ecosystem.
2. ARO AI ChatBot Azure OpenAI Components
2.1 Azure OpenAI Overview
Azure OpenAI Service offers convenient REST API access to OpenAI’s advanced language models, such as GPT-4, GPT-3.5-Turbo, and Embeddings series. The GPT-4 and GPT-3.5-Turbo models are now widely available. These models can be tailored for various tasks like content creation, summarization, semantic search, and translating natural language to code. Users can utilize the service via REST APIs, Python SDK, or the web-based interface in Azure OpenAI Studio.
Azure Red Hat OpenShift delivers on-demand, fully managed OpenShift clusters that are highly available, with joint monitoring and operation by Microsoft and Red Hat. At its core, it utilizes Kubernetes. OpenShift enhances Kubernetes by adding valuable features, transforming it into a turnkey container platform as a service (PaaS) that greatly enhances the experiences of both developers and operators.
2.1.1 Comparing Azure OpenAI vs OpenAI
Azure OpenAI Service provides customers access to sophisticated language AI models like OpenAI GPT-4, GPT-3, Codex, DALL-E, and Whisper, all within the secure and reliable environment of Azure. In collaboration with OpenAI, Azure OpenAI co-develops APIs, ensuring seamless compatibility and transition between models.
With Azure OpenAI, customers benefit from the robust security features of Microsoft Azure while utilizing identical models as OpenAI. Azure OpenAI offers private networking, availability in specific regions, and responsible AI content filtering, enhancing the overall user experience and ensuring responsible usage of AI technology.
2.2 Gradio
A highly effective approach for showcasing your machine learning model, API, or data science workflow to others involves developing an interactive application that enables users or peers to experiment with the demo directly through their web browsers.
Gradio, a Python library, offers a streamlined solution for constructing such demos and facilitating easy sharing. In many cases, achieving this only requires a concise snippet of code.
If you want to take a look of other Gradio Apps, check my Blog Post around Deploying and Testing Machine Learning Applications in Kubernetes with Gradio!
2.3 LangChain
LangChain stands as a versatile framework designed for developing applications driven by language models. Its core functionalities enable applications to:
-
Contextual Awareness: LangChain facilitates the connection of language models to diverse sources of context, including prompt instructions, few-shot examples, and relevant content. This enables applications to respond in a manner grounded in the provided context, enhancing their overall effectiveness.
-
Intelligent Reasoning: By leveraging LangChain, applications gain the ability to rely on language models for reasoning. This involves determining appropriate responses and actions based on the provided context, enhancing the application’s decision-making process significantly.
The key value propositions offered by LangChain include:
-
Modular Components: LangChain provides abstract structures for interacting with language models, coupled with a variety of implementations for each structure. These components are modular and user-friendly, ensuring ease of use, whether integrated within the LangChain framework or utilized independently.
-
Pre-configured Chains: LangChain offers pre-built chains, which are structured combinations of components designed to accomplish specific high-level tasks. These ready-to-use chains simplify the application development process, allowing developers to focus on specific functionalities without the hassle of building complex architectures from scratch.
In essence, LangChain streamlines the development process, offering a flexible and efficient approach to creating context-aware and intelligent applications powered by language models.
2.4 Azure Red Hat OpenShift
The Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift service enables to deploy fully managed OpenShift clusters.
Azure Red Hat OpenShift is jointly engineered, operated, and supported by Red Hat and Microsoft to provide an integrated support experience. There are no virtual machines to operate, and no patching is required. Master, infrastructure, and application nodes are patched, updated, and monitored on your behalf by Red Hat and Microsoft. Your Azure Red Hat OpenShift clusters are deployed into your Azure subscription and are included on your Azure bill.
When you deploy Azure Red Hat on OpenShift 4, the entire cluster is contained within a virtual network. Within this virtual network, your master nodes and workers nodes each live in their own subnet. Each subnet uses an internal load balancer and a public load balancer.
3. ARO AI ChatBot with Azure OpenAI: Demo Analysis
Let’s shift our focus from theory to practical application and explore how this ChatBot operates and interacts in real-time.
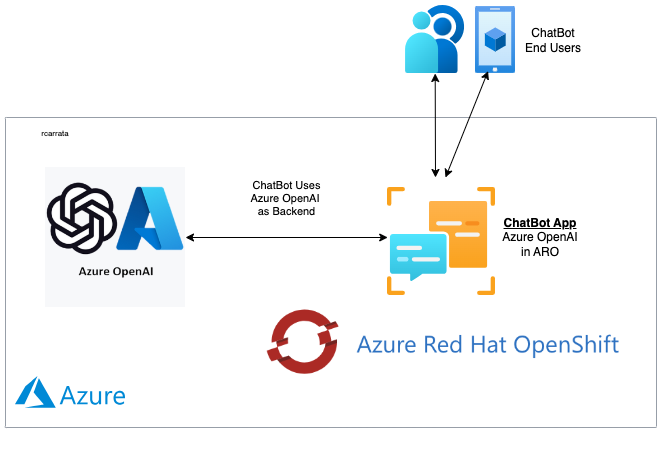
Once deployed within our Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster, the ARO AI ChatBot application becomes accessible through a specific URL. This application, powered by Azure OpenAI as its backend, offers a user-friendly interface for interaction.
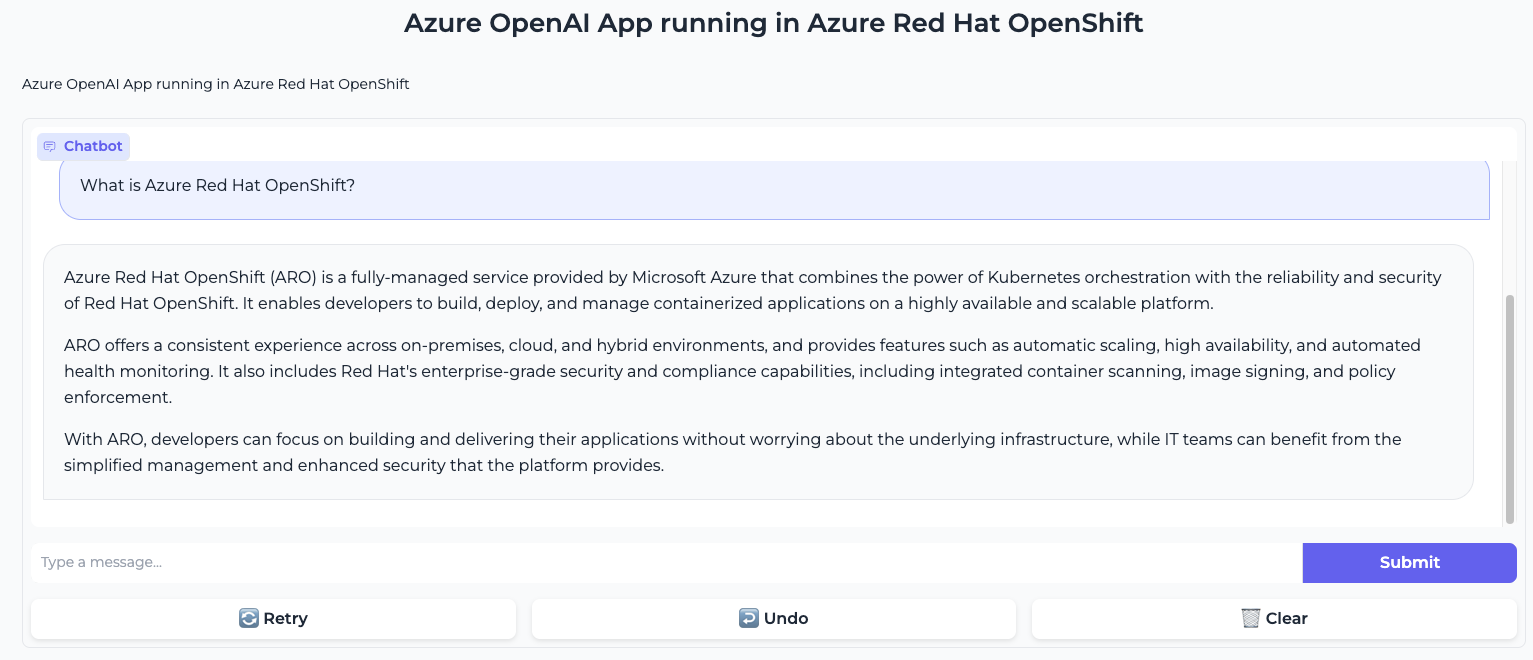
In the provided images, we witness the ChatBot in action. In the first screenshot, we posed a straightforward yet intriguing question: “What is Azure Red Hat OpenShift?”.
The Gradio App, functioning as the frontend, utilizes LangChain libraries internally to connect with our deployed GPT 3.5 model in Azure OpenAI:
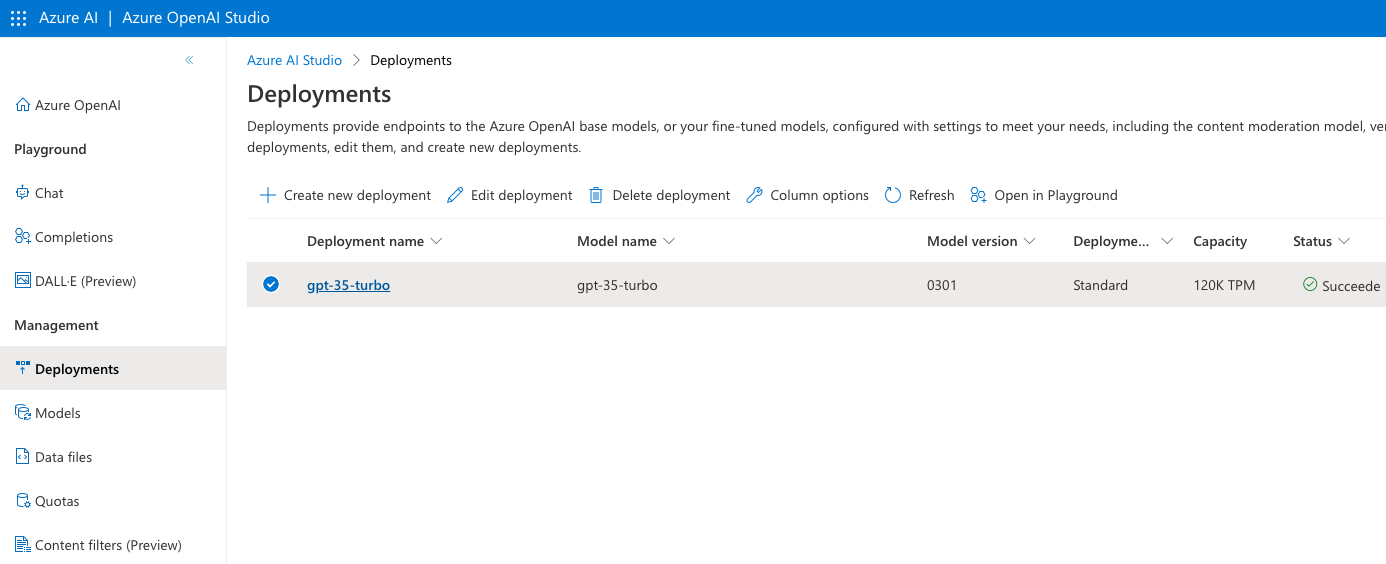
Specifically, we deployed the gpt-35-turbo model, utilizing the 0301 version, hosted in the Azure France Central region.
But how can we be certain that our ChatBot is effectively utilizing the Azure OpenAI GPT Model as its backend?
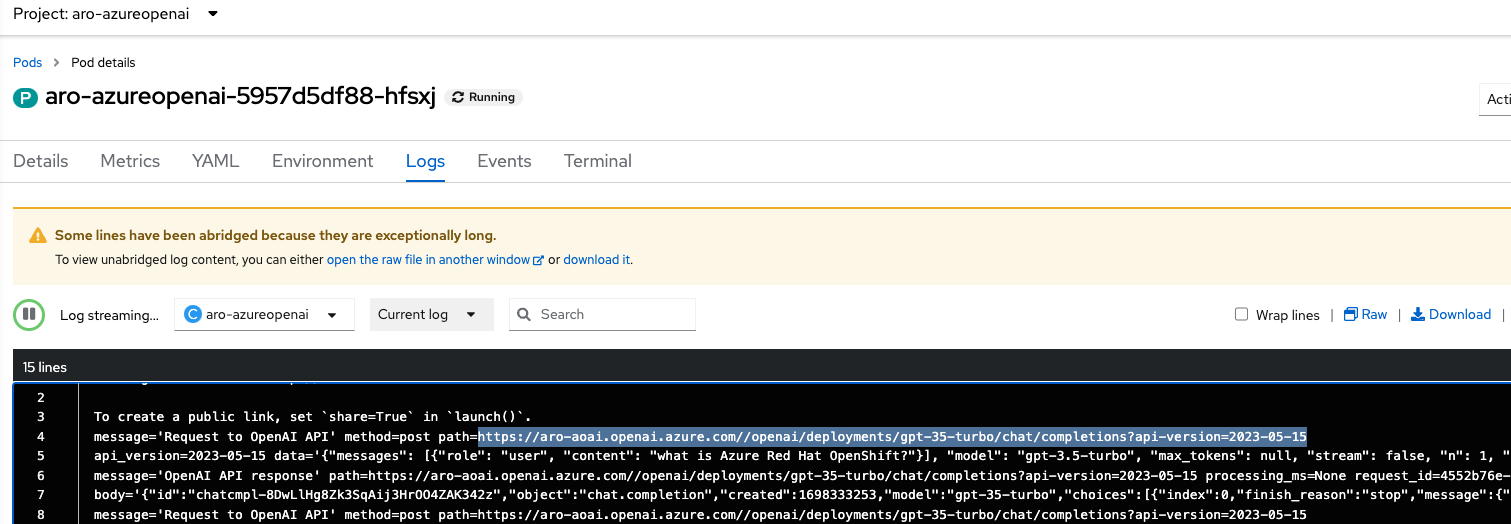
To validate this, we can delve into the ARO Console and inspect the ChatBot’s logs:
Upon careful observation, the logs reveal the ChatBot’s process: it sends the Human Message using LangChain libraries to the Azure OpenAI URL. The GPT Model in Azure OpenAI generates the response, which is then relayed back to the “human,” completing the ChatBot’s interaction loop.
This seamless integration showcases the synergy between LangChain libraries, Gradio frontend, and Azure OpenAI backend, enabling a dynamic and interactive user experience.
In our upcoming blog post, we will delve deeply into the integration components of the demonstration and provide comprehensive insights into how you can deploy your very own version in your Azure Red Hat OpenShift cluster!
Stay tuned for an in-depth exploration of the deployment process and harness the power of this integration for your projects.
NOTE: Opinions expressed in this blog are my own and do not necessarily reflect that of the company I work for.
Happy AI/ML-ing!